
Methodology
Introduction
The methodology outlines 16 indicators to examine and assess the 200 most influential ICT companies’ policies, processes, performance and disclosure across the breadth of the digital system, from hardware to software and telecommunication services to platforms.
The critical digital inclusion themes covered by the benchmark include access, skills, use and innovation. In addition the WBA social transformation indicators have been integrated into this year’s Digital Inclusion Benchmark. The social indicators add a more comprehensive view of company performance by incorporating aspects such as human rights, decent work and acting ethically into the benchmark.
Digital technology can be a powerful enabler of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, divides around access to technology, digital skills, inclusive technology development and exposure to online risks and harms persist around the world, slowing the potential to achieve the SDGs. Companies, while varied in their approach and levels of commitment, are evolving rapidly in how they view information and communications technologies (ICTs) as a tool for sustainable development. Acting as a global accountability mechanism, publicly available benchmarks are a vital first step towards shedding light on the reality of corporate impact in this area.
Read the methodologyClassifying digital companies by industry
Digital companies vary widely. Some manufacture equipment, some provide telecommunication services, some offer information technology (IT) or ICT-enabled services while others carry out two or more of these activities. Given the significant functional differences among digital companies, it is analytically important to classify them into key categories. Digital companies are categorised in various ways depending on the classification source. The Sustainable Accounting Standards Board (SASB) sector and industry classification and UN International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities are used as references.
Most of the 200 companies fall into the technology and communications sector category, which includes the following industries: electronic manufacturing services and original design manufacturing; hardware; internet media and services; semiconductors; software and IT services; and telecommunication services.
There are other sectors with industries featuring digital companies: consumer goods (e-commerce); infrastructure (data centres); financials (digital finance); and services (digital media).
Companies are then classified into three broad industries:
- hardware, consisting of the manufacture of digital goods such as end-user devices, network equipment and semiconductors
- telecommunication services;
- IT services, consisting of software applications, data centres, cloud computing and platform services.
When companies provide diverse products, they are classified in the layer from which they derived the most revenues in the most recent accounting year.
Digital companies by region
Companies with corporate headquarters in fifty-one economies are represented in the benchmark with a global footprint extending to almost the entire planet, either through subsidiaries, supply chains and countries where the products are bought and used. Companies have been classified into geographies for analytical purposes. Due to the large number of digital companies included from mainland China and the United States, they are shown separately.
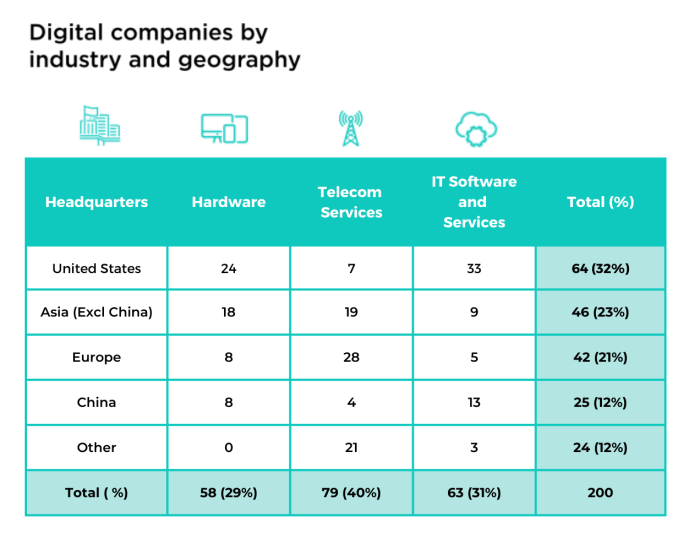
In the figure ‘Other’ refers to Latin America and the Caribbean, Middle East, Pacific, Sub-Saharan Africa and Canada. Companies headquartered in Hong Kong and Taiwan, have been classified in Asia due to the different legal environments they operate under.
Scoring guidelines
The Digital Inclusion Benchmark consists of 16 indicators equally divided into four measurement areas: access, skills, use and innovation. This document describes how the indicators and measurement areas are scored to result in an overall benchmark score. Find the scoring guidelines below.
Download scoring guidelinesDetailed company scores per indicator
Scores for each company are publicly available at the indicator and measurement area level for all stakeholders. Individual company results are presented in company scorecards, and scores against each of the 16 indicators are disclosed in a detailed scoring sheet. The Core Social Indicators are also included.