Measurement finding
Governance and strategy
This measurement area looks at a company’s overall commitment to gender equality and women’s empowerment across its full value chain.

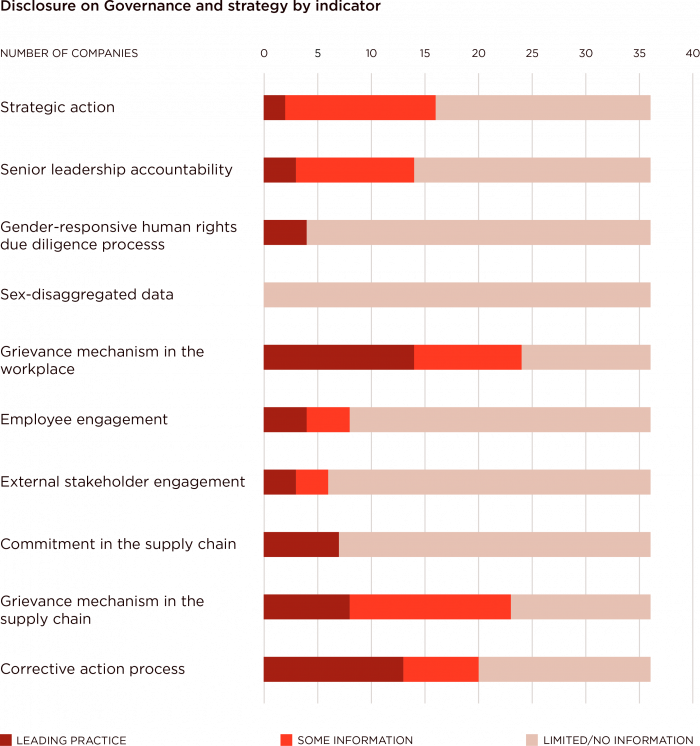
Twenty-nine companies (81%) share some information on governance and strategy with regard to their policies and practices either in the workplace, in the supply chain or at the corporate level.
Many companies (24 companies, 67%) report on grievance mechanisms that take into account the specific needs of women employees and supply chain workers, as well as on their corrective action process in the supply chain and on their strategic action to drive gender equality and women’s empowerment.
Fewer than half the companies (14 companies, 39%) provide information in relation to senior leadership accountability for their gender efforts, employee and external stakeholder engagement on gender impacts, their gender-responsive human rights due diligence processes, and their commitment to gender equality and women’s empowerment in the supply chain.
No company reports the breakdown of data by gender on the number of grievance reported, the gender balance of its workforce across various levels leaderships, the percentage of employees participating in training programmes, turnover and absenteeism, pay data, remediation of violence and harassment grievances, the total procurement spend that is directed to women-owned businesses, and injuries, fatalities and absenteeism of workers in the supply chain.
1. Strategic action
There are 12 companies (33%) that have made a public commitment to gender equality and women’s empowerment, ten of which are signatories to the United Nations Women’s Empowerment Principles. Thirteen companies (36%) have a gender strategy that goes beyond support for diversity and inclusion and focuses on organisation-wide gender representation and specifies the initiatives for achieving this. Only seven companies have established specific, time-bound targets that go beyond increasing gender diversity in senior positions. Only two companies (Ascena Retail Group and Kering) have undertaken a gender audit and obtained a third-party certification for gender equality.
2. Senior leadership accountability
Fourteen companies (39%) have one or more individuals responsible for their diversity and inclusion or sustainability efforts, which includes gender, and often these individuals report to the board of directors. For three companies (LVMH, Ralph Lauren and VF Corporation), gender equality and women’s empowerment issues are monitored by the board of directors.
3. Gender-responsive human rights due diligence process
Only four companies (Fast Retailing, H&M, Gap and Walmart) have a gender-responsive human rights due diligence process where they screen for three or more gender-related risks as part of their human rights due diligence process and assess those risks to be salient. The most common gender-related risks screened for by companies are sexual harassment, gender-based violence, gender discrimination and human trafficking. No information was found as to whether companies consult with affected and potentially affected women in the workplace and supply chain, women’s organisations (including grass-roots organisations), women human rights defenders or other gender experts as part of the risk identification and assessment process.
4. Sex-disaggregated data
No company reports the breakdown of data by gender on the number of grievance reported, the gender balance of its workforce across various levels leaderships, the percentage of employees participating in training programmes, turnover and absenteeism, pay data, remediation of violence and harassment grievances, the total procurement spend that is directed to women-owned businesses, and injuries, fatalities and absenteeism of workers in the supply chain.
5. Grievance mechanism
Twenty-four companies (67%) disclose information on their grievance mechanism. Moreover, 13 companies have a mechanism with at least six elements, such as confidentiality, anonymous reporting, verbal submission of grievances, alternate access to a party concerning the grievance if the perpetrator is the direct supervisor of the aggrieved party, and protection against non-retaliation. Although these elements are present in the grievance mechanism, there is not an explicit reference to women or gender.
6. Employee engagement
Eight companies (22%) disclose information showing that they engage with their employees on gender issues, such as compensation, parental leave, discrimination, harassment and informing their overall strategies but only four companies share information that shows that this feedback is integrated into company policies and practices: Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail, Fast Retailing, LVMH, and Walmart.
7. External stakeholder engagement
Six companies (17%) are engaging with external stakeholders on gender issues but only three (Associated British Foods, Fast Retailing and VF Corporation) publish information that indicates this feedback is incorporated into their wider business strategy.
8. Commitment in the supply chain
Seven companies (20%) publish information where they signal a commitment towards gender equality and women’s empowerment in the supply chain: Ascena Retail Group, Gap, Inditex, Levi’s, Marks and Spencer Group, PVH and Ralph Lauren. However, only Levi’s requires suppliers to have processes in place to listen to workers and identify local needs in areas such as hygiene and sanitation, sexual and reproductive health, economic empowerment, financial education and access to financial products and services, violence and harassment, and working hours.
9. Grievance mechanism in the supply chain
Twenty-three companies (64%) report information which shows they require suppliers to have a grievance mechanism for their workers or make their own grievance mechanism available to workers. However, only eight companies ensure that the grievance mechanism is adapted to address the needs of supply chain workers, for instance by ensuring that workers are aware of the grievance mechanism and that it is available in all the languages spoken by workers: Associated British Foods, Kering, L Brands, Lojas Renner, Marks and Spencer Group, PVH, Target and Walmart.
10. Corrective action process in the supply chain
Twenty companies (56%) publish information showing that they screen for gender-related issues among their suppliers as part of their auditing processes. However, only 13 companies identified three or more gender-related issues that either require corrective action plans to be put in place with a supplier or result in the termination of a supplier relationship. Issues that are commonly audited by companies include sexual harassment and discrimination on the basis of marital status and pregnancy.
